Lesson Plan > Lesson 40 > Mathematics
Lesson 40 covers:
- Elementary Level: Word Problems with Addition and Subtraction
- Mid Level: Comparing and Ordering Fractions
- High Level: Combining Like Terms and Using the Distributive Property
Elementary Level (Kinder to Grade 2)

Subject: Word Problems with Addition and Subtraction
Alignment with Standards:
- 1.OA.A.1: Use addition and subtraction within 20 to solve word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions.
- 1.OA.A.2: Solve word problems that call for addition of three whole numbers whose sum is less than or equal to 20.
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Read and understand simple word problems.
- Identify whether a problem requires addition or subtraction.
- Write a corresponding number sentence (equation).
- Solve word problems within 20 using manipulatives or drawings.
Materials Needed
- Counters (e.g., buttons, beads, blocks)
- Whiteboard and markers
- Printed word problem worksheets (with visuals)
- Number line (0-20)
- Pencils and paper
Lesson Procedure
1. Warm-Up (5-10 minutes)
Objective: Activate prior knowledge of addition and subtraction.
- Counting Practice: Count forward and backward from 0 to 20.
- Quick Equations: Solve simple equations (e.g., 5 + 3 = ?, 8 – 2 = ?).
- Discussion: Ask, “When do we use addition? When do we use subtraction?”
2. Introduction to Word Problems (10-15 minutes)
Objective: Teach how to identify key information in word problems.
- Example Problem (Display on whiteboard or image prompt):
“Liam has 7 apples. He gives 3 apples to his friend. How many apples does Liam have left?”
- Guided Steps:
- Understand the problem: What is happening? (Liam starts with 7, gives away 3.)
- Choose the operation: Is it adding or taking away? (Subtraction)
- Write the equation: 7 – 3 = ?
- Solve using counters or a number line.
3. Hands-On Practice (15-20 minutes)
Objective: Solve word problems using manipulatives and drawings.
- Activity 1: Acting Out Problems
- Use counters to model problems (e.g., “Emma has 6 cookies. She buys 4 more. How many does she have now?”).
- Activity 2: Draw It Out
- Students draw pictures to represent word problems (e.g., “There are 9 birds on a tree. 5 fly away. How many are left?”).
4. Independent Practice (10-15 minutes)
Objective: Apply skills to solve problems independently.
- Provide a worksheet with 4-5 word problems (mix of addition and subtraction).
- Example problems:
- “There are 5 red balloons and 4 blue balloons. How many balloons are there in all?”
- “Noah has 12 toy cars. He gives 6 to his brother. How many cars does Noah have now?”
5. Wrap-Up & Review (5-10 minutes)
- Discussion: Ask students to explain how they solved one problem.
- Exit Question: “If you have 8 candies and eat 2, how many are left?”
- Optional Extension: Create their own word problems for a family member to solve.
Assessment
- Observation: Check if students correctly use counters/drawings.
- Worksheet Accuracy: Review answers for correct equations and solutions.
- Verbal Explanation: Ask students to explain their reasoning.
Additional Tips for Homeschoolers
- Real-Life Connections: Use toys, snacks, or household items for problem-solving.
- Games: Play “Word Problem Charades” where a child acts out a scenario, and the parent writes the equation.
- Repetition: Practice daily with different contexts (e.g., animals, candies, books).
Mid Level (Grade 3 to 5)

Subject: Comparing and Ordering Fractions
Alignment with Standards:
- 4.NF.A.2: Compare two fractions with different numerators and denominators, e.g., by creating common denominators or numerators, or by comparing to a benchmark fraction such as ½. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole.
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Compare two fractions using <, >, = symbols.
- Use visual models (fraction bars/circles) to justify comparisons.
- Apply strategies like common denominators or benchmark fractions.
- Order a set of fractions from least to greatest or greatest to least.
Materials Needed
- Fraction bars or circles (printed or physical manipulatives)
- Whiteboard and markers
- Printed worksheets with fraction comparison exercises
- Number line (0 to 1, divided into halves, thirds, fourths, etc.)
- Pencils and paper
Lesson Procedure
1. Warm-Up (5-10 minutes)
Objective: Review fraction basics and activate prior knowledge.
- Fraction Quick Check:
- “What is the numerator? Denominator?”
- “Which is larger: ½ or ¼? How do you know?”
- Visual Matching: Show fraction models (e.g., ¾ vs. ⅔) and ask which looks bigger.
2. Direct Instruction (15-20 minutes)
Objective: Teach three strategies for comparing fractions.
Strategy 1: Visual Models (Fraction Bars/Circles)
- Display two fractions (e.g., ⅖ vs. ⅗).
- Shade fraction bars to compare:
- “Which has more shaded parts? So, ⅖ __ ⅗?” (Answer: ⅖ < ⅗)
Strategy 2: Common Denominators
- Compare ½ vs. ⅓ by converting to sixths:
- ½ = ³⁄₆, ⅓ = ²⁄₆ → ³⁄₆ > ²⁄₆, so ½ > ⅓.
Strategy 3: Benchmark Fractions (Compare to ½, 1)
- Example: ⅜ vs. ⅘
- ⅜ < ½ (since ⁴⁄₈ = ½), but ⅘ > ½ → ⅜ < ⅘.
3. Guided Practice (15 minutes)
Objective: Apply strategies with teacher support.
- Activity 1: Hands-On Comparison
- Use fraction manipulatives to compare pairs (e.g., ⅔ vs. ⁴⁄₆).
- Activity 2: Number Line Ordering
- Place ¼, ½, ⅞ on a number line to visualize size.
4. Independent Practice (15 minutes)
Objective: Reinforce learning through worksheets and games.
- Worksheet: 8-10 problems comparing fractions (e.g., “Write <, >, or =: ⁴⁄₅ ___ ⅗”).
- Sorting Game: Cut out fractions and order them least to greatest.
5. Wrap-Up & Discussion (5-10 minutes)
- Exit Ticket: “Explain how you know ⅔ > ⅖.”
- Real-World Connection: “If you eat ⅖ of a pizza and your friend eats ½, who ate more?”
Assessment
- Observation: Check if students use strategies correctly.
- Worksheet Accuracy: Review for correct use of symbols.
- Verbal Explanation: Ask students to justify their answers.
Additional Tips for Homeschoolers
- Cooking Math: Compare ingredient measurements (e.g., ⅓ cup vs. ½ cup).
- Tech Integration: Use free online fraction games (e.g., Fractions on SplashLearn).
- Challenge: Introduce mixed numbers (e.g., 1½ vs. 1⅓).
High Level (Grade 6 to 8)
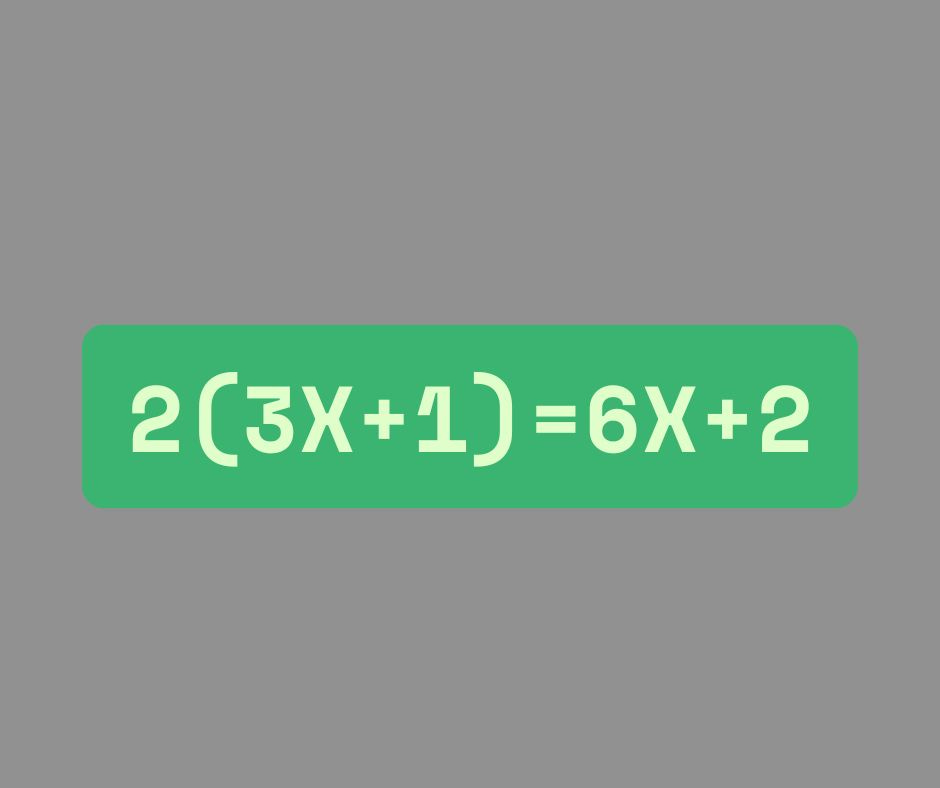
Subject: Combining Like Terms and Using the Distributive Property
Alignment with Standards:
- 7.EE.A.1: Apply properties of operations to add, subtract, factor, and expand linear expressions with rational coefficients.
- 7.NS.A.1: Apply and extend previous understandings of operations with fractions to add, subtract, multiply, and divide rational numbers.
Lesson Objectives
By the end of this lesson, students will be able to:
- Identify like terms in an algebraic expression.
- Combine like terms to simplify expressions (e.g., 3x+5x=8×3x+5x=8x).
- Apply the distributive property to expand and factor expressions (e.g., 4(2x+3)=8x+124(2x+3)=8x+12).
- Solve real-world problems using these skills.
Materials Needed
- Whiteboard & markers
- Algebra tiles (or printed cutouts)
- Worksheets with practice problems
- Colored pencils (for highlighting like terms)
- Real-world scenario cards (e.g., shopping discounts, perimeter problems)
Lesson Procedure
1. Warm-Up (10 minutes)
Objective: Review basic algebraic vocabulary.
- Quick Definitions:
- “What is a term? (E.g., 3x3x, −5y2−5y2)”
- “What does like terms mean? (Same variable & exponent)”
- Example Sort:
- Given terms (2x,5y,−3x,72x,5y,−3x,7), group like terms.
2. Direct Instruction (20 minutes)
Objective: Teach combining like terms and distributive property with examples.
Part 1: Combining Like Terms
- Example 1: 4x+2x=6×4x+2x=6x (Same variable → Add coefficients).
- Example 2: 5y−3y+7=2y+75y−3y+7=2y+7 (Only yy terms combine).
- Common Mistake: 3x+4y3x+4y cannot be combined!
Part 2: Distributive Property
- Expanding: 3(2x+5)=6x+153(2x+5)=6x+15.
- Factoring: 10x+15=5(2x+3)10x+15=5(2x+3).
- Visual Aid: Use algebra tiles to model 2(x+4)2(x+4).
3. Guided Practice (20 minutes)
Objective: Apply concepts with scaffolding.
- Activity 1: Algebra Tile Exploration
- Simplify 3x+2+x−53x+2+x−5 using tiles (group xx’s and constants).
- Activity 2: Error Analysis
- Fix mistakes in a worked problem (e.g., 4(3x−2)=12x−24(3x−2)=12x−2 → Missing full distribution).
4. Independent Practice (20 minutes)
Objective: Reinforce skills through varied problems.
- Worksheet:
- Combine like terms: 7a−3b+2a+57a−3b+2a+5.
- Apply distributive property: −2(4x−7)−2(4x−7).
- Challenge: Factor 12y+1812y+18.
- Real-World Task:
- “A rectangle has length 3x+23x+2 and width 55. Write and simplify its perimeter expression.”
5. Wrap-Up & Reflection (10 minutes)
- Exit Ticket:
- Simplify: 5(2y−3)+4y5(2y−3)+4y.
- “Explain how the distributive property helps solve problems.”
- Discussion: Share real-world uses (e.g., sales tax, bulk pricing).
Assessment
- Worksheet Accuracy: Check for correct simplification/factoring.
- Verbal Explanation: Ask students to justify steps in a problem.
- Real-World Task: Assess applied understanding (e.g., perimeter problem).
Additional Tips for Homeschoolers
- Real-Life Math: Calculate family meal costs with discounts (e.g., 22 pizzas at each + delivery fee).
- Game: Play “Expression Match”—pair simplified and expanded forms.
- Tech Tool: Use Desmos or Khan Academy for interactive practice.












LEAVE A COMMENT